 Spina Bifida is one of the most common types of neural tube birth defects. You may have heard of it before, but do you really know what it is or what causes it?
Spina Bifida is when the embryonic neural tube, consisting of the brain, spinal cord and meninges (the protective covering that surrounds the brain and spinal cord), fails to close completely. The neural tube is an embryo’s developing brain and spinal cord. This tube should close around the 28th day after fertilization occurs.
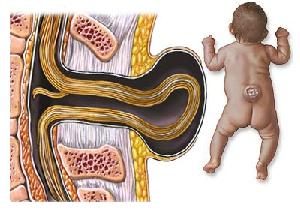
Some of the vertebrae that surrounds the spinal cord doesn’t form completely and remains open or unfused. This gap can vary in size and severity. If the gap is large enough, it actually allows the spinal cord to protrude through the vertebrae, where it is no longer protected and remains exposed.
Spina Bifida is one of the most common types of neural tube birth defects. You may have heard of it before, but do you really know what it is or what causes it?
Spina Bifida is when the embryonic neural tube, consisting of the brain, spinal cord and meninges (the protective covering that surrounds the brain and spinal cord), fails to close completely. The neural tube is an embryo’s developing brain and spinal cord. This tube should close around the 28th day after fertilization occurs.
Some of the vertebrae that surrounds the spinal cord doesn’t form completely and remains open or unfused. This gap can vary in size and severity. If the gap is large enough, it actually allows the spinal cord to protrude through the vertebrae, where it is no longer protected and remains exposed.
Types of Spina Bifida
There are four types of Spina Bifida, ranging from mild to severe. The mildest form may go undetected throughout a person’s entire life and the most severe form can be quite debilitating, causing partial to complete paralysis.- Occulta – This is the mildest form and there are usually no outer signs that anything is wrong. Since there is usually only a very small gap in the vertebrae, the spinal cord does not stick through the vertebrae. A lot of people who have this type of Spina Bifida don’t even know they have this defect because they may not have any symptoms.
- Closed neural tube defect – This type consists of a wide range of defects where the fat, bones and membranes that make up the cord are not formed correctly. These can range in severity from no noticeable symptoms to nerve damage. Babies will usually have a mark on their back that signals that something might be wrong. It can be anything from a dimple, a tuft of hair, a lump or even an opening in the skin.
- Meningocele – In this form the meninges sticks out of the unfused vertebrae (gaps between the vertebrae). Since the nerves remain undamaged in this type of Spina Bifida, long term effects are unlikely. It can result in a problem known as tethered spinal cord syndrome, but it is very rare. In this situation, the spinal cord is stretched abnormally and causes nerve problems. With Meningocele, the protrusion may or may not be covered with skin. There will usually be a small fluid filled sac protruding from the back and it is usually covered by skin.
- Myelomeningocele – This is the most severe form. The spinal cord sticks out through an opening in the vertebrae. Some forms leave the nerves in the spinal cord completely exposed as they are not covered with any sort of protective covering. Due to nerve damage at the site, it causes partial or complete paralysis below the area of exposure. The higher up the damage is on the spinal cord, the more area of body that will be effected. Exposed nerves can also become easily infected. Just like Meningocele, there will usually be a small sac that protrudes from the back, except it will most likely not be covered by any skin.
Detection and Treatment of Spina Bifida
Thanks to today’s advancements in medical technology, the detection and of Spina Bifida may be done early in the pregnancy. Early prenatal care is so important for this reason. The sooner you know something is wrong, the sooner you can take the necessary steps to correct any problems. One of the tests that is used to detect birth defects is the AFP (Alpha-Fetoprotein) test. This test is done by either taking a blood sample from the mother or through an amniocentesis. Spina Bifida can also be detected through a detailed ultrasound. In mild cases though, it may be very hard to detect and may go completely unnoticed. Depending upon the situation, some cases of Spina Bifida can be corrected through intrauterine surgery. This is done while the baby is still inside the mother’s uterus. If surgery is not possible through this method, they will wait until the baby is born to fix any problems.How can Spina Bifida be prevented?
Since this defect occurs in the first month of fetal development, before conception is even known in a lot of cases, it is important you take the necessary precautions before you even try to get pregnant.- Taking Folic Acid BEFORE conception, can help reduce this birth defect significantly (up to 75%).
- Folic acid can be found in such things as prenatal supplements, “enriched” products including cereals, dark green leafy vegetables, beans, oranges/orange juice, avocado and strawberries.
- Other external causes can increase the chances of Spina Bifida. These include such things as seizure medications, fevers or high body temperatures (such as from hot showers or hot tubs). If you can, take all possible steps to avoid these risk factors and let your doctor be aware of such things if you have already been exposed.
- Genetics has also been linked to an increased risk of this defect. If the mother has Spina Bifida, or has experienced another pregnancy with a neural tube defect, there is a higher chance of this defect occurring. If these situations are known, you can plan ahead and take extra precautions before trying to conceive. Your doctor will usually have you take extra doses of Folic Acid to help lower the chances of any problems. Speak to your doctor to find out how much you should be taking.
What Is Spina Bifida



